Problem Identification and Selection
- May 19, 2021
- 13 min read
It was our first weekend since we were introduced to systems. By then we got a hold on how systems work, why the problems associated with them are called wicked, it was the right moment for us to give some thoughts on real-world problems.

We were asked to identify real-world problems through all the different perspectives such as social, economical, environmental, regional, global, technological and many more which needed immediate attention and all the groups came up with more than 100 problems. With all the multifaceted problems in the world today, it is difficult to solve all of the problems. However, it is crucial to prioritize certain issues over others to dedicate enough resources to combat the top problems in the world that can be solved.
I am sharing here a few of the problems that our team has identified to prioritise them in the further steps.
We have divided problems further into 6 Categories
Regional Problems
Global
Science & Technology
Space
Speculative
Others
*click on images for source
Regional Problems
1. Water Crisis in Kolar, Karnataka
Kolar, a district in Karnataka, which completely depends on underground water is now facing drought as the water level has sunk deeper. There are two current projects going on to bring back water in the district by using treated sewage water from Bangalore to refill the sunk undergrounds and another project which brings pure water from around 300 km apart from the state.
2. Desertification of Bangalore
Every year since 2012, Bangalore has been hit by drought; last year Karnataka, of which Bangalore is the capital, received its lowest rainfall level in four decades. But the changing climate is not exclusively to blame for Bangalore’s water problems. The city’s growth, hustled along by its tech sector, made it ripe for the crisis. Echoing urban patterns around the world, Bangalore’s population nearly doubled from 5.7 million in 2001 to 10.5 million today.
3. Population explosion in Bengaluru
Whether it’s for its job opportunities, lovely weather or affinity towards startups and new businesses, Bangalore has been a haven for people across the country. So much so that half the population in the city is made up of migrants, going by the 2011 census and recently released migration data! According to the census report, out of the 96.2 lakh people in Bangalore, 44.3 lakh are classified as migrants – that’s 50.6% if you consider just the urban population! Work and marriage are the oft-cited reasons for moving, as per the report.
4. Bengaluru has world’s worst traffic congestion, says study
Bengaluru is the most traffic-congested city in the world, says the latest traffic index published by TomTom, the Dutch location technology specialist that competes with Google Maps.
Peak time commuters in Bengaluru spend an extra 10 days and three hours stuck in traffic each year, compared to the time they would have taken if they were commuting during uncongested conditions. That’s an extra 71% of travel time.
5. Sterlite issue in Tamil Nadu
The copper smelter plant at Thoothukudi was shut down in 2018 by Tamil Nadu Pollution Control Board over environmental violations. On May 22, 2018, at least 13 people were killed and several others were injured when the state police fired at people who had taken out a demonstration against the construction of a new smelter plant by Vedanta.
Design for conflict, Now government opens the plant for producing oxygen for the period of four months. Based on the requirement of oxygen, the period might be extended. The electricity supply to the oxygen plants would be cut by the government after the specified period. Play of political parties and people.
6. Childs Play - COVID generation
No child's play - Indian journal of practical paediatrics stating several alarming factors affecting children- lockdown prevents scheduled immunisation from taking place leading to the outbreak of vaccine-preventable diseases- The cage syndrome- the learning crisis
The most critical part is the online education income for low economy group people and lower-middle-class people.
7. India and Sri Lanka's violent fight over fish
As in the past, fishermen from Rameswaram and nearby coasts continue to sail towards Talaimannar and Katchatheevu coasts, a region famous for rich maritime resources in Sri Lanka. Plenty of catch in this oceanic region had triggered a proliferation of fishing trawlers in the Tamil Nadu coast in the past three decades. There were many favourable reasons too for Indian fishermen as their access to Sri Lankan waters was easier at the time of the Sri Lankan civil war.
8. Kaveri River water dispute
The sharing of waters of the Kaveri River has been the source of a serious conflict between the two Indian states of Tamil Nadu and Karnataka. The genesis of this conflict rests in two agreements in 1892 and 1924 between the Madras Presidency and the Kingdom of Mysore
9. Child abduction/trafficking in India
According to a report by the National Human Rights Commission of India, 40,000 children are abducted each year, leaving 11,000 untraced.
NGO's estimate that between 12,000 and 50,000 women and children are trafficked into the country annually from neighbouring nations as a part of the sex trade.
10. KGF mines Closure
The Kolar gold mines were nationalized in 1956 and provided a total of over 900 tonnes of gold. They were closed by the Indian government on 28 February 2001 for environmental and economic reasons; food, water and shelter were scarce, and production did not justify the investment.
11. Locusts attack in India
It is the first time the suburb city of Gurgaon (Gurugram) has seen a locust invasion.
Footage on social media showed tens of thousands of insects flying over buildings and landing on rooftops.
India is witnessing its worst locust invasion in decades. The swarms, which originate in the Horn of Africa, have devoured crops in several states.
12. iPhone manufacturer Wistron violence in Kolar, Karnataka
Worker unrest following the non-redressal of payment and overtime issues at a new factory of Wistron Infocomm Manufacturing India Pvt Ltd, a subsidiary of Wistron Corporation, the Taiwan-headquartered computers and computer peripherals firm that manufactures iPhones for Apple and other products, resulted in a riot at the plant on December 12.
13. Climate change and sea heat up in the Bay of Bengal
Climate change amplifies the cyclonic storms that typically form in the northern Indian Ocean. Increasing sea surface temperatures can make cyclones more powerful. Warmer oceans mean there is higher rainfall during storms. Rising sea levels due to global warming make for higher storm surges, which reach larger inland areas. Higher temperatures also lead to cyclones forming much faster, as was the case with Nisarga and Amphan.
Global Problems
1. Eating less Meat won't save the Planet.
It’s commonplace today to blame meat for everything from cancer to global warming. We’re rightly scared about our health and our world.
• Should we eat meat at all?
• Is there a “best” diet for humans? Or is there a spectrum of optimal human nutrition?
• Can meat be part of a sustainable food system?
• Can a sustainable food system exist without meat and animal contributions, both nutritionally and environmentally?
• How important are ethics in the story of human nutrition and sustainability?
2. High Carb to Low Carb to Keto to Carnivore. What's Next?
As we look to 2050, when we’ll need to feed two billion more people, the question of which diet is best has taken on new urgency. The foods we choose to eat in the coming decades will have dramatic ramifications for the planet. Simply put, a diet that revolves around meat and dairy, a way of eating that’s on the rise throughout the developing world, will take a greater toll on the world’s resources than one that revolves around unrefined grains, nuts, fruits, and vegetables.
3. The global coffee crisis is coming

The world's coffee industry is in crisis. This May, coffee prices fell to their lowest point in over a decade at $0.88 (£0.70) per pound.
The dip is largely due to two years of surplus from Brazil, the world's largest coffee producer, which has had a serious impact on growers around the world by pushing millions of kilograms of beans onto the market. Economic issues in coffee-producing regions like Central America and Africa are also at work.
4. Food waste is the world's dumbest problem

America wastes roughly 40 per cent of its food.1 Of the estimated 125 to 160 billion pounds of food that goes to waste every year, much of it is perfectly edible and nutritious. Food is lost or wasted for a variety of reasons: bad weather, processing problems, overproduction and unstable markets cause food loss long before it arrives in a grocery store, while overbuying, poor planning and confusion over labels and safety contribute to food waste at stores and in homes.2 Food waste also has a staggering price tag, costing this country approximately $218 billion per year.
5. Quality of Indian Education
Poor quality education is leading to poor learning outcomes in India, ultimately pushing children out of the education system and leaving them vulnerable to child labour, abuse and violence. Many classrooms continue to be characterized by teacher-centred rote learning, corporal punishment and discrimination.
The number of universities has increased in the last four decades. a number of higher education students increased 12 times. But no university is among 200 IQSranking.
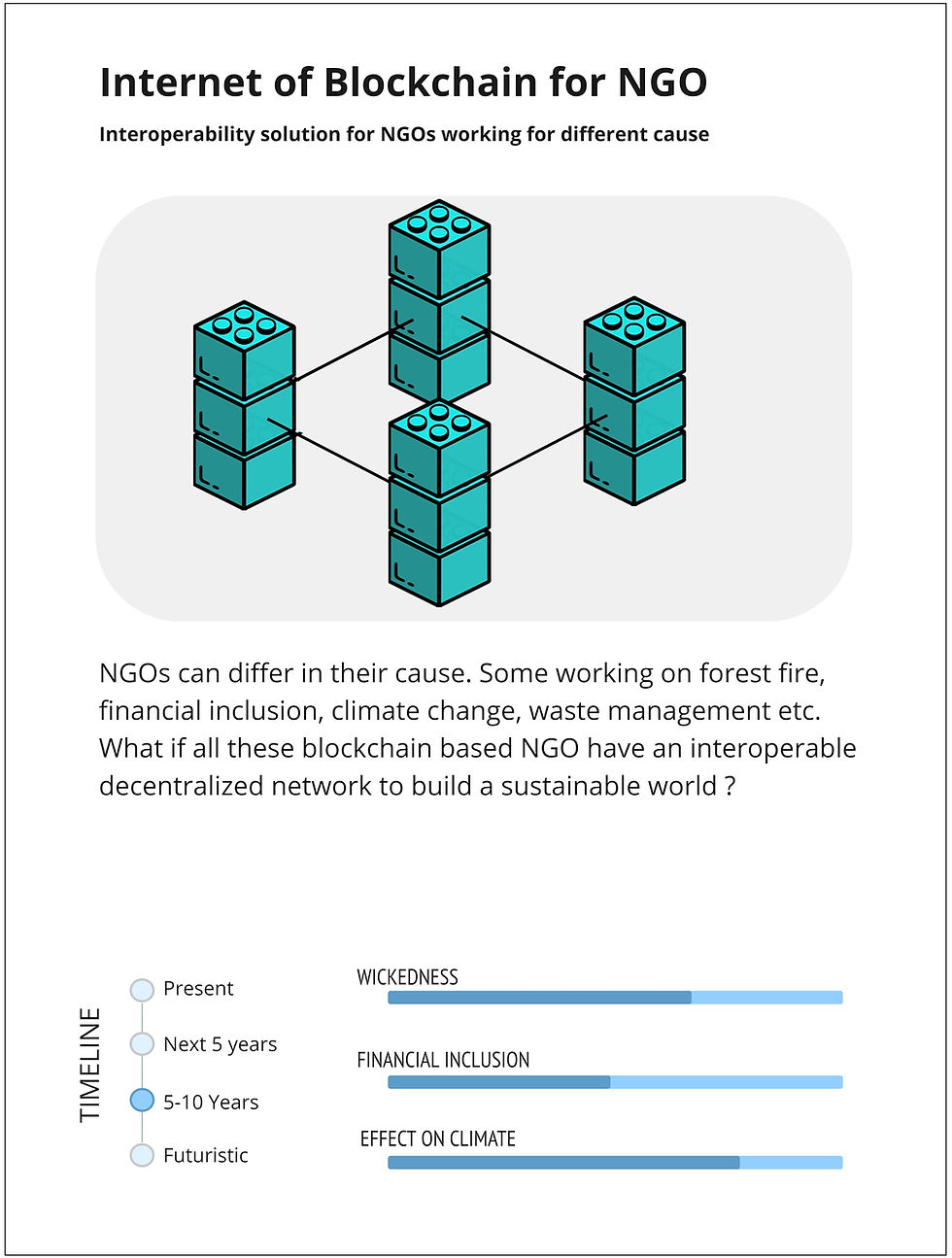
6. Providing Food for Everybody
India has 2% decline in the land area in the last two decades and productivity growth in the food industry is growing 2 per cent. one-third of what produced is wasted. The demand in an increase in food will be 10 times more in the year 2050. so tackling farming is a difficulty and one of the major wicked problem.
At the same time, the decrease in the yields is predicted up to 12%.
7. Nuclear Energy waste hazard
Thirty-five years after the disaster, the nuclear industry is Ukraine’s most reliable economic lifeline. But critics say it faces a perennial crisis caused by corruption, safety problems and politicised decision-making.
8. Open Approach in Spying
MI5 officially joined Instagram on Thursday, making it the latest intelligence agency to try its hand at social media. The agency hopes its account, @Mi5official, will debunk myths about the art of spying, help explain the world of intelligence to the masses and highlight the agency’s history, it said in a statement.
9. AFRICA: e-waste output reaches alarming levels
According to the UN's Global E-waste Monitor 2020, 2.9 million waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) was generated in 2019 on the African continent. A real danger to both health and the environment, as Africa has a serious lack of policies and structures to manage and recycle WEEE.
10. Problem with recycling of the e-waste
“The big problem the electronics industry is facing as a whole is products are getting lighter and lighter,” iFixit’s Kyle Wiens said. “This is great for consumers but a nightmare for recyclers.” Smaller, lighter products can be tricky to take apart, and yield a lower volume of raw materials.
11. Effect of Environmental Chemicals on Human Health
Humans and animals have always been exposed to chemicals in our environment - natural products in foods, smoke from cooking fires, sewage in drinking water, pesticides from plants. However, the dramatic increases in industrialization over the past three centuries have dramatically changed both the quality and the number of human exposures, to both natural and synthetic chemicals
12. Climate change emerges as the culprit in food poisoning outbreaks
The last decade has been particularly rough on the leafy greens industry. You’re certainly aware of the multiple outbreaks of foodborne pathogens like E. coli, which have killed hundreds and sickened thousands more. Cattle feedlots have emerged as a major source of contamination for leafy green contamination but over at Eater, Jenny Zhang homes in on another culprit: climate change. Though it’s an emergent field of study and many unknowns remain, some early observations include: Rising temperatures can help E. coli and salmonella proliferate; those same hot temps provoke cattle into shedding pathogens more readily, and climate change-related flooding can rapidly spread contamination into water supplies used in irrigation. Think of climate change as both an amplification of existing hazards, as well as a potential trigger for things we can’t foresee.
13. Satellites show the world's glaciers melting faster than ever
Glaciers are melting more quickly, losing 31 per cent more snow and ice per year than they did 15 years ago, according to three-dimensional satellite measurements of all the world's mountain glaciers.
Using 20 years of recently declassified satellite data, scientists calculated that the world's 220,000 mountain glaciers have been losing more than 298 billion metric tonnes of ice and snow per year since 2015, according to a study in Wednesday's journal Nature.
The annual melt rate from 2015 to 2019 is 71 billion metric tonnes more per year than it was from 2000 to 2004.
Global thinning rates, different from the volume of water lost, doubled in the last 20 years.
Half the world's glacial loss is coming from the United States and Canada.
14. Wild Geoengineering Plan to Refreeze Arctic Sea Ice
The paper, published in Earth’s Futures on Thursday, takes its inspiration from a previous study that first raised the prospect of an Arctic geoengineering project. That study outlined a proposal to install wind turbines across the Arctic that would power pumps to draw water to the surface of the remaining sea ice, where it would refreeze more quickly than from the bottom-up.
Science & Technolgy
1. The real cost of smart speakers

Smart speakers offer convenience; much of their popularity can simply be chalked up to that. But tech companies are also clearly pushing the technology onto consumers hard, sometimes selling smart speakers at rock-bottom prices, and building the “listening” technology that drives them into all sorts of other products, from headphones to doorbells. And a big reason for that is all the data that they produce.
2. Cybersecurity threats
Cybersecurity threats are more prevalent than ever before with increased digital activities. This has drawn many hackers, who are becoming more sophisticated and are targeting many more businesses. Vital Information, such as trade secrets, price-sensitive information, HR records, and many others are more vulnerable. Strengthening cybersecurity laws can maintain equilibrium.
3. Artificial Intelligence Implementation
Businesses, especially those in the tech industry, are having trouble implementing AI. If you’ve used and improved upon your AI over the years, you’re likely having an easier time adjusting. But new online businesses test multiple AI programs at once and it’s causing communication and data mix-ups. As businesses settle with specific programs and learn what works for them, we will see improvement.
So implementing AI is leads to many security breach problems in the future. A designing is essential in this sector.
4. Grid – Connected Solar PV System in India
Grid-interconnected Photovoltaic (PV) source is one of the fastest developing and most prominent renewable energy sources in the globe. The main reason behind this is the remarkable progress in the semiconductor manufacturing domain. Also, the reduction in the price of PV modules helps in the starting of economic incentives or subsidies. Although the core of a PV system is the PV cell (or PV generator), the power electronics sector plays a major role as a cutting edge technology for efficient photovoltaic system control, hence transferring the generated power to the grid supply.
5. CHIMERA: HUMAN MONKEY HYBRID. IS IT ETHICAL?
In the latest advance, researchers in the U.S. and China announced earlier this month that they made embryos that combined human and monkey cells for the first time. So far, these human-monkey chimaeras are no more than bundles of budding cells in a lab dish, but the implications are far-reaching, ethics experts say. The use of primates so closely related to humans raises concerns about unintended consequences, animal welfare and the moral status of hybrid embryos, even if the scientific value of the work may be quite high.
6. Muon: The fifth fundamental force
Fundamental particles are the building blocks of the universe. They’re smaller than an atom. And, the muon is one of them. It’s like an electron, but 200 times heavier.
The particle is relatively unstable and only has a lifespan of 2.2 microseconds before it decays into an electron and two super-lightweight particles called neutrinos.
Space
1. A Trip to Space
Experience Earth’s wonders from space—from the Great Barrier Reef, Himalayas, Amazon River, and Giza’s Pyramids by day, to the glow of city lights, lightning storms, and the Aurora Borealis by night. Dragon fully orbits the Earth every 90 minutes, making a highly customized flight path possible. Fly over your hometown, famous landmarks and other places meaningful to you.
2. What Elon Musk's 42,000 Satellites Could Do To Earth
Over the next few decades, Elon Musk is hoping to send 42,000 Starlink satellites to space. With these satellites, SpaceX hopes to bring high-speed satellite internet to every corner of the world. But experts worry it may come at a hefty cost, blocking astronomers' views and potentially space exploration for decades.
3. Human space exploration and cost outrun for mars exploration

Human space exploration is dangerous at all levels. After more than fifty years of humans travelling from Earth to space, the risk of space flight is similar to that of climbing Mount Everest.
Mars is an unforgiving environment where a small mistake or accident can result in large failure, injury, and death. Every component must work perfectly. Every system (and its backup) must function without fail or human life is at risk.
The proposed Mars One budget includes a large safety margin to take into account significant mission failures as well as smaller but costly failures of components on Mars.
4. UFO: Seeing is Believing
The US Department of Defense has released three declassified videos of "unexplained aerial phenomena". The Pentagon said it wanted to "clear up any misconceptions by the public on whether or not the footage that has been circulating was real".
The videos had already been leaked in 2007 and 2017.
5. Ingenuity: First Martian Flight
NASA's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter made another successful takeoff and landing Sunday. The flight was partially captured on video by NASA's Perseverance Mars rover. The helicopter took off and flew out of the rover's field of vision while completing a flight plan that took it 164 feet (50 meters).
Can this be a key to efficiently map the Martian surface?
Speculative
1. Will We Ever Visit Other Stars?

The nearest star to Earth, Proxima Centauri, lies 4.2 light-years from us — so far away that it would take tens of thousands of years to get there using current technology. And most stars, of course, are much more distant than that; our Milky Way galaxy is about 100,000 light-years wide.
2. Warp Drive: Interstellar Travel
The closest star to Earth is Proxima Centauri. It is about 4.25 light-years away or about 25 trillion miles (40 trillion km). The fastest-ever spacecraft, the now-in-space Parker Solar Probe will reach a top speed of 450,000 mph. It would take just 20 seconds to go from Los Angeles to New York City at that speed, but it would take the solar probe about 6,633 years to reach Earth’s nearest neighbouring solar system.
If humanity ever wants to travel easily between stars, people will need to go faster than light. But so far, faster-than-light travel is possible only in science fiction.
3. Is Dark Web Dangerous?
The Internet is sizable with millions of web pages, databases, and servers all run 24 hours a day. But the so-called "visible" Internet (aka surface web or open web) — sites that can be found using search engines like Google and Yahoo — is just the tip of the iceberg.
There are several terms surrounding the non-visible Web, but it's worth knowing how they differ if you're planning to browse off the beaten path.
4. Psychedelic drugs and the future of mental health care
Though psychedelic drugs remain illegal, guided ceremonies, or sessions, are happening across the country, especially in major cities like New York, San Francisco, and Los Angeles. Guiding itself has become a viable profession, both underground and above, as more Americans seek out safe, structured environments to use psychedelics for spiritual growth and psychological healing. This new world of psychedelic-assisted therapy functions as a kind of parallel mental health service. Access to it remains limited, but it’s evolving quicker than you might expect.
Though psychedelic drugs remain illegal, guided ceremonies, or sessions, are happening across the country, especially in major cities like New York, San Francisco, and Los Angeles. Guiding itself has become a viable profession, both underground and above, as more Americans seek out safe, structured environments to use psychedelics for spiritual growth and psychological healing. This new world of psychedelic-assisted therapy functions as a kind of parallel mental health service. Access to it remains limited, but it’s evolving quicker than you might expect.








































Comments